In ancient Egypt, the concept of divine judgement played a significant role in their religious beliefs. The Egyptians believed that after death, their souls would be judged by a specific god who would determine their fate in the afterlife. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of the Egyptian god of judgement and explore various aspects related to this deity and its influence on ancient Egyptian culture and beyond.
Understanding the Concept of Divine Judgement in Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egyptian society was deeply rooted in religion, and the concept of divine judgement was an integral part of their belief system. For the Egyptians, the afterlife held great importance, and they believed that their actions in life would determine their fate in the realm of the dead. Divine judgement served as a means to separate the righteous from the wicked, ensuring that each soul would be judged accordingly.
The Egyptians believed that the gods played a significant role in the judgement process. These deities were not only responsible for overseeing the judgement itself but also for maintaining cosmic balance and order in the universe.
The Role of Deities in Ancient Egyptian Society
The ancient Egyptians worshiped a pantheon of gods and goddesses, each with their own unique traits and responsibilities. These deities were believed to have the power to control various aspects of life, including the afterlife and the judgement process. One such deity was Ma’at, the goddess of truth, justice, and cosmic order.
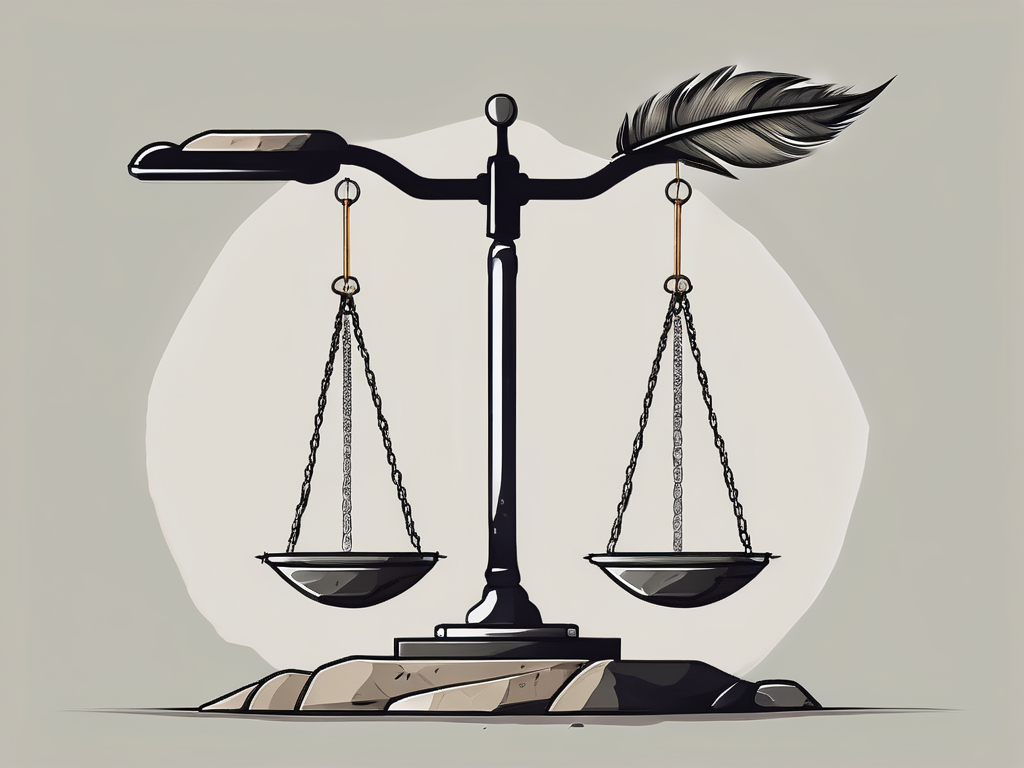
Ma’at, often depicted with an ostrich feather on her head, was seen as the embodiment of balance and harmony. It was believed that Ma’at would weigh the heart of the deceased against her feather during the judgement process. If the heart was found to be lighter than the feather, it meant that the person had lived a righteous life and would be granted access to the afterlife. However, if the heart were heavier, it indicated a life lived in sin, leading to eternal punishment.
Another important deity in the judgement process was Osiris, the god of the afterlife and the underworld. Osiris was not only responsible for judging the souls but also for granting them eternal life in the afterlife. He was often depicted as a mummified figure, symbolizing his connection to death and resurrection.
The Concept of Afterlife and Judgement in Egyptian Mythology
Ancient Egyptian mythology played a crucial role in shaping their beliefs about the afterlife and the concept of judgement. The Egyptians believed in an intricate system of underworld realms, with each soul destined to be judged and allocated a specific place based on their life’s deeds.
The Egyptian Book of the Dead, a collection of funerary texts, provided guidance and prayers for the deceased on their journey to the afterlife. These texts contained spells and rituals aimed at securing the soul’s safe passage through the judgement process and beyond.
According to Egyptian mythology, the judgement process took place in the Hall of Ma’at, where the deceased would stand before a tribunal of gods and goddesses. The heart of the deceased would be weighed on a scale against the feather of Ma’at, while Thoth, the god of wisdom and writing, recorded the results.
If the heart was found to be pure and lighter than the feather, the deceased would be declared justified and would proceed to the blissful afterlife. However, if the heart was heavy with sin, it would be devoured by Ammit, a fearsome creature with the head of a crocodile, the body of a lion, and the hindquarters of a hippopotamus. This would result in eternal punishment and the denial of an afterlife.
It is important to note that the judgement process was not limited to the weighing of the heart. The tribunal of gods and goddesses also considered the individual’s overall conduct in life, including their adherence to moral and ethical principles. The Egyptians believed that the gods possessed an intimate knowledge of every person’s thoughts, actions, and intentions, making it impossible to deceive or escape judgement.
In conclusion, the concept of divine judgement in ancient Egypt was a fundamental aspect of their religious beliefs. The Egyptians believed that their actions in life would determine their fate in the afterlife, and the gods played a crucial role in overseeing the judgement process. Through the weighing of the heart and the consideration of one’s overall conduct, the righteous were rewarded with eternal life, while the wicked faced eternal punishment. This belief in divine judgement served as a moral compass for the ancient Egyptians, guiding their actions and shaping their society.
An Overview of the Egyptian God of Judgement
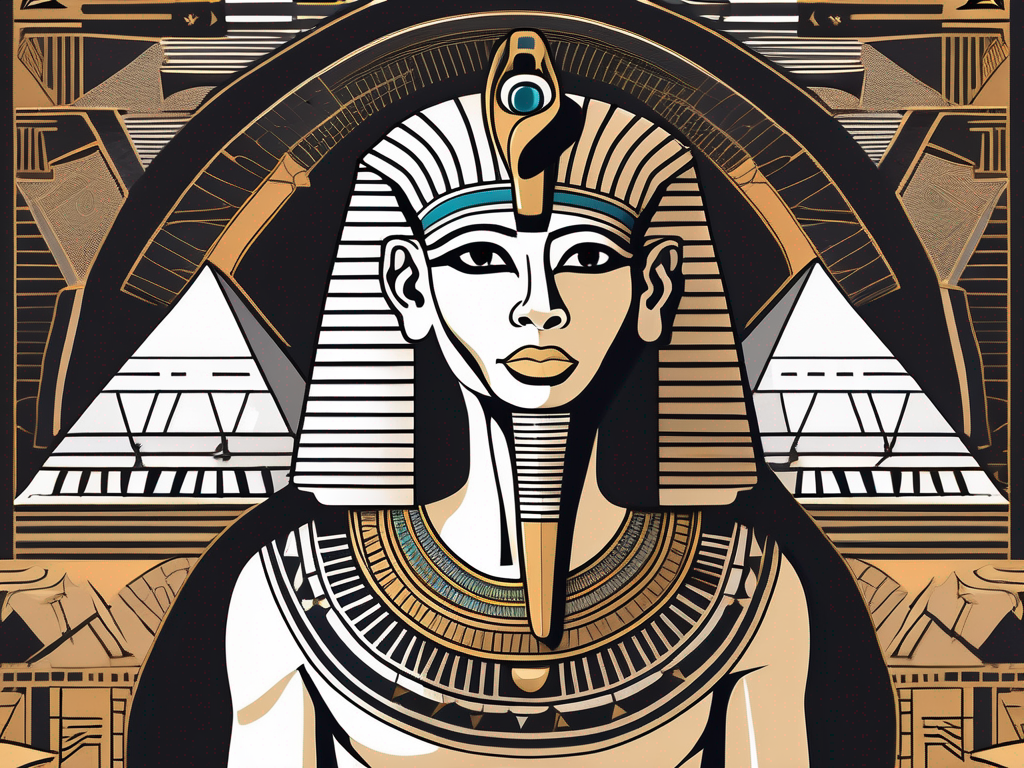
One of the key figures associated with divine judgement in ancient Egypt was Osiris, the god of the underworld, rebirth, and fertility. Osiris played a pivotal role in the judgement process, overseeing the weighing of the heart and the ultimate fate of the soul.
The Iconography of the Egyptian God of Judgement
Osiris was often depicted as a mummified figure, symbolizing his connection to the realm of the dead. He wore a white crown with ostrich feathers, representing his role as the god of judgement and justice. His skin often had a greenish hue, symbolizing rebirth and fertility.
Osiris was frequently portrayed holding a crook and a flail, symbols of his authority and power over life and death. The crook represented his role as a shepherd of souls, guiding the righteous to their rightful place in the afterlife, while the flail signified his ability to punish the wicked.
The Powers and Responsibilities of the Egyptian God of Judgement
As the god of judgement, Osiris had the power to decide the eternal fate of the deceased. He presided over the weighing of the heart ceremony, where he determined whether the individual had led a righteous life or not.
Osiris was also a symbol of transformation and rebirth. He represented the cycle of life, death, and resurrection, offering hope to those who sought redemption and a chance for eternal life in the afterworld.
The Rituals and Ceremonies Associated with the Egyptian God of Judgement
Rituals and ceremonies held a significant place in ancient Egyptian religion, especially those related to the judgement process. These rituals were believed to help the deceased in their journey to the afterlife and create a favorable outcome during the judgement.
The Importance of Rituals in Ancient Egyptian Religion
Ancient Egyptians believed that performing rituals and following specific religious practices were essential for a successful journey to the afterlife. These rituals included mummification, burial practices, and the recitation of specific prayers and spells.
By adhering to these rituals, individuals sought to receive the favor of the gods, particularly Osiris, ensuring a positive judgement outcome and a place among the righteous in the afterlife.
The Process of Judgement in Ancient Egyptian Beliefs
The judgement process in ancient Egypt was a highly symbolic and intricate affair. The deceased would be brought before Osiris, where their heart would be weighed against the feather of Ma’at on the scales of justice.
During the weighing ceremony, the deceased would recite spells and affirmations, proclaiming their innocence and declaring their righteous actions in life. The judges, including Osiris, would closely observe the ceremony, determining the worthiness of the deceased based on the results.
The Influence of the Egyptian God of Judgement on Modern Culture
Even in modern times, the Egyptian god of judgement continues to captivate the imagination of artists, writers, and filmmakers. The allure of ancient Egyptian mythology and the complex concept of divine judgement have found their way into various forms of contemporary media.
The Egyptian God of Judgement in Literature and Film
Books and movies often feature adaptations or interpretations of ancient Egyptian mythology. The character of Osiris, with his association with judgement and the afterlife, has been portrayed in numerous works, further showcasing the enduring fascination with this deity.
The Modern Interpretation of the Egyptian God of Judgement
In modern times, the concept of divine judgement has taken on different meanings and interpretations. Some see it as a moral or ethical evaluation of one’s actions, while others view it as a metaphorical representation of the consequences we face for our choices.
The Comparison of the Egyptian God of Judgement with Other Cultures
Ancient Egypt was not the only civilization to have a concept of divine judgement. Various cultures around the world have developed their own beliefs and deities associated with the judgement process.
Similarities and Differences in Divine Judgement Concepts
Comparing the Egyptian god of judgement with other cultures’ deities and beliefs about divine judgement can reveal intriguing similarities and differences. Exploring these diverse concepts provides a broader understanding of the human quest for justice and salvation.
The Impact of Egyptian Beliefs on Other Ancient Civilizations
Ancient Egypt’s religious beliefs, including those related to divine judgement, had a profound influence on neighboring and distant cultures. The idea of judgement and the role of gods in determining one’s fate in the afterlife can be traced to various civilizations that interacted with ancient Egypt.
In conclusion, the concept of divine judgement was an integral part of ancient Egyptian religious beliefs. The Egyptian god of judgement, Osiris, played a crucial role in overseeing the judgement process and determining the eternal fate of the deceased. Rituals, ceremonies, and mythology surrounding Osiris and the concept of divine judgement continue to fascinate and inspire people in modern times. By exploring these ancient beliefs, we gain insights into the human quest for justice, redemption, and the afterlife.